AIR-LAID WEB FORMATION

Ramandeep Singh
B.Tech, Dept. of Textile Engineering
Giani Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus,
Bathinda, Punjab, India
Email: rmnsandhu3335@gmail.com

Ramandeep Singh
B.Tech, Dept. of Textile Engineering
Giani Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus,
Bathinda, Punjab, India
Email: rmnsandhu3335@gmail.com
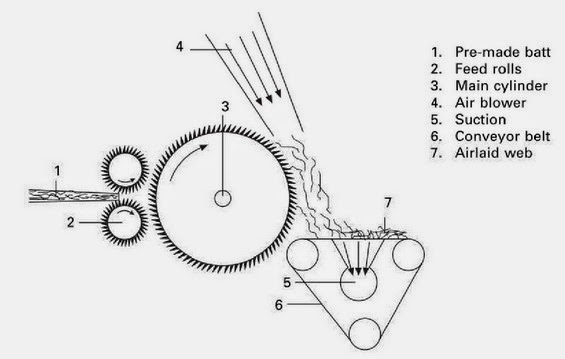
PRINCIPLE OF WEB FORMATION IN A SIMPLE AIR LAYING PROCESS
RAW MATERIAL - Natural or man-made textile fibre (cut length >25 mm)
- Short cut fibres (generally
- Wood pulp (1.5–6 mm)
- The fibers are oriented randomly on the fabric surface – isotropic structure.
- Voluminious webs can be produced
- The range of the area weight is wider (15 – 250 g/m2) but the mass uniformity of light air laid (up to 30 g/m2) is bad.
- Wide variety of processable fibers
- Low level of opening fiber material by lickerin roller Thus is suitable to use pre-opened fibers or combine air laid with card machine – Random card machine.
- Variable structures of web in width of layer due to irregular air flow close to walls of duct . This problem requires high quality design of duct.
- Possible entangling of fibers in air stream. This problem can be reduced by increasing the ratio air/fibers which nevertheless means decrease in performance and increase of energy consumption due to high volume of flowing air.
QA = K.P.L2/D
Thus is suitable to use short fibers for this technology.
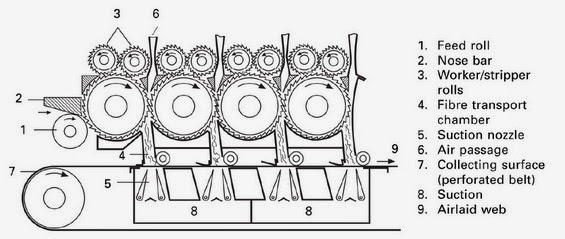
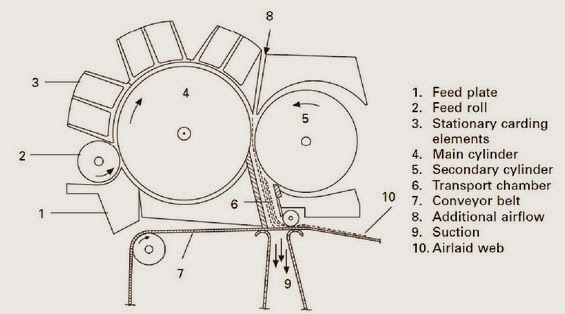
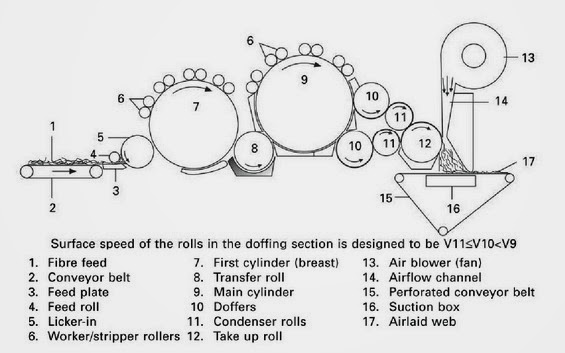
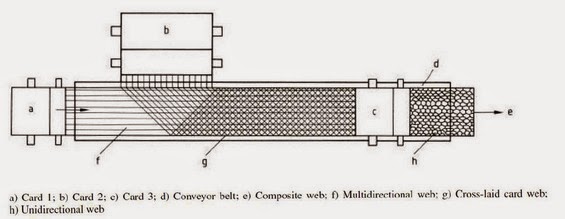
Random cards – combination of air laid and carding technology
A major objective of this combination is isotropic textile fabric (random orientation of fibers) with good mass uniformity of light fabrics and with high production speed. - The first part – card machine opens perfectly fibrous material so single fibers are as a output.
- The second part – air laid system uses the centrifugal force to strip the fibers off a roller and. put them down on an air controlled scrim belt.
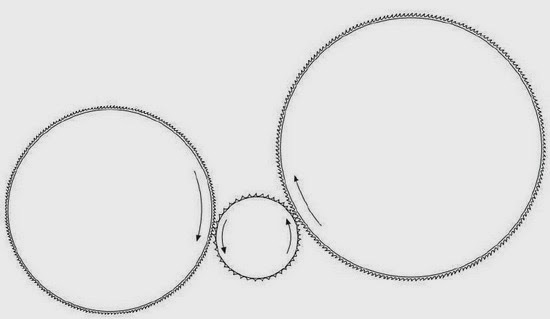
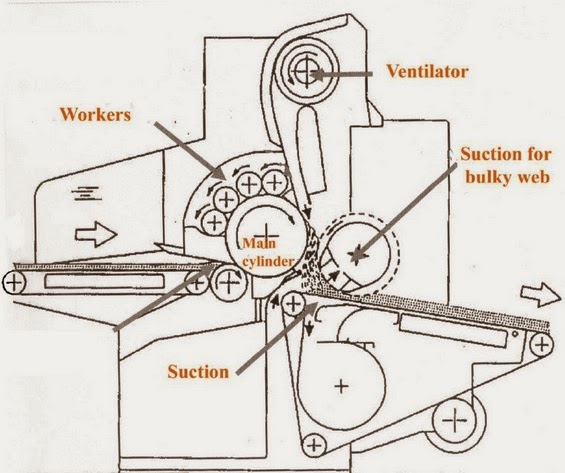
Airlaid function of random card: 1) Random roller between main cylinder and doffer, which rotate in the opposite direction of the main cylinder.
MAIN VARIATIONS OF RANDOM CARDS Main variations of random cards II. 2) Centrifugal force of mean cylinder strips the fibers off.
AIR LAID AND RANDOM CARDS: USED FIBERS
Synthetic fibres, viscose, cotton and blends thereof; natural fibres such as flax, hemp, sisal etc.; Reclaimed textile waste and shoddy, cellulose pulp 1.7 - 2000dtex. Max. 120 mm staple length
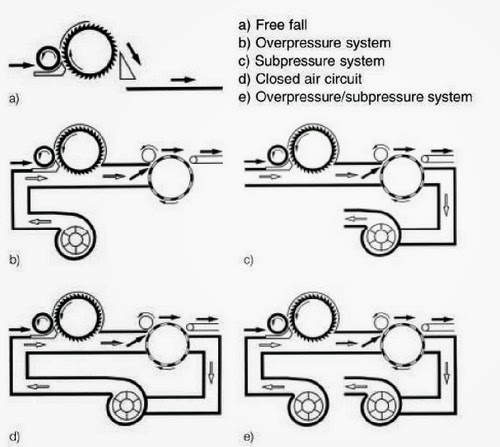
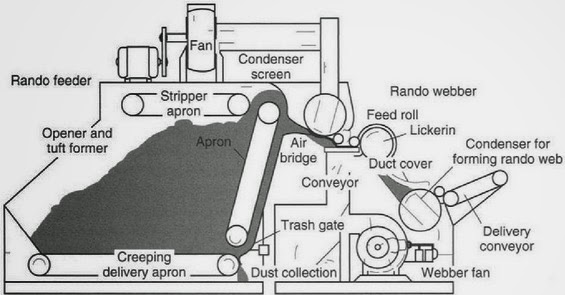
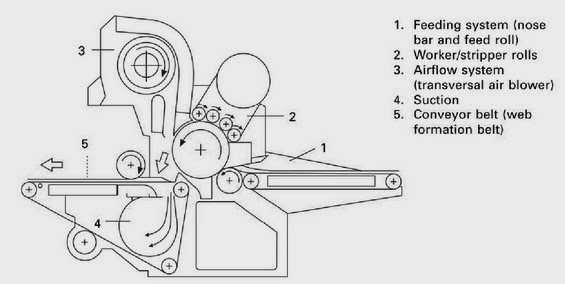
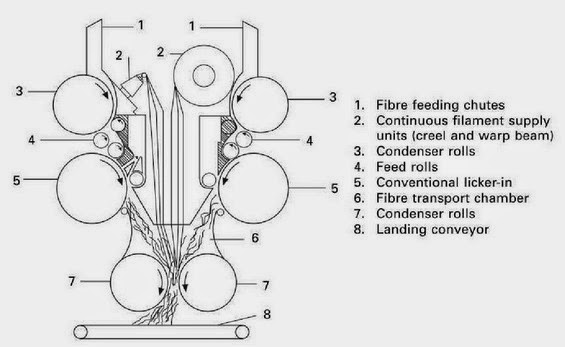
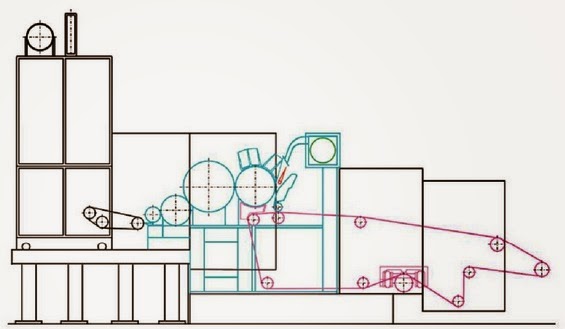
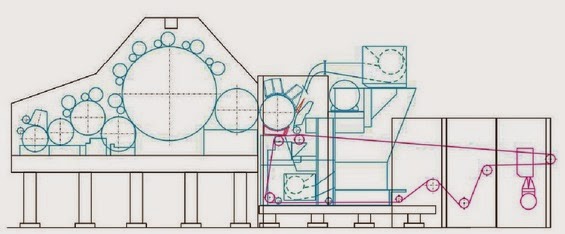
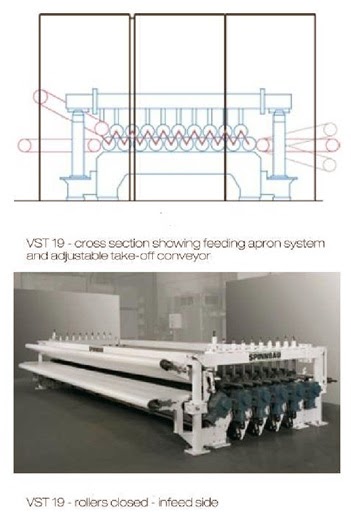
FEEDING SYSTEM OF RANDO WEBBER
RANDO-WEBBER SYSTEMS WITH PERFORATED SCREEN
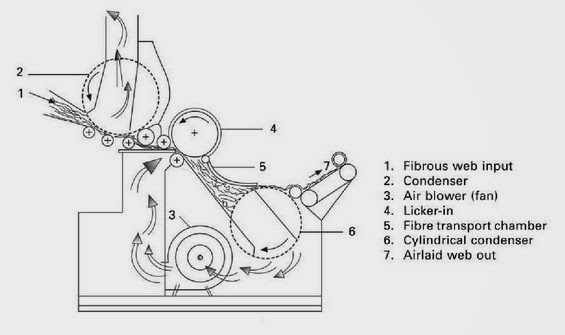
RANDO-WEBBER SYSTEMS WITH CYLINDRICAL CONDENSERS
Rando-webber - Relatively narrow widths up to about two metres
- Webs of 10– 3000 g/m 2
- Virgin or recycled fibres
- Filtration, home furnishings, automotive fabrics, insulation and some medical specialities
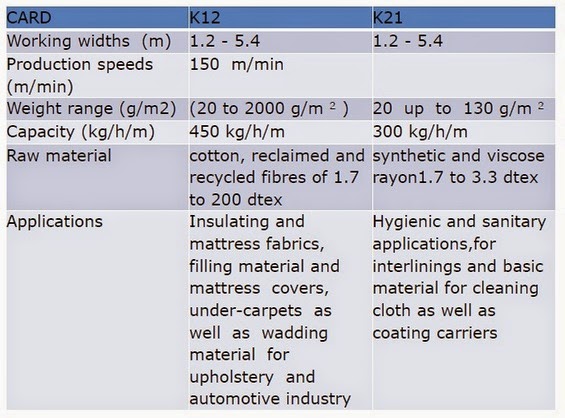
- K12 is more particularly suited to coarse fibres (10–110 dtex), Basic weight range 20– 2000 g/m 2
- K21 is more particularly suited to synthetic and viscose rayon fibers of (1.7–3.3 dtex), Basic weight range 10–100 g/m 2
- Air velocity ( 140 m/s)
- Surface speed of the cylinder ( 20–60 m/s)
- Staple fibres ranging from 13–75 mm
- Typical MD/CD ratio of 1.2–1.5:1
- Production rate of 200–260 kg/h/m
- Web weights of 35–200 g/m 2
- Fibre types cotton, viscose rayon, PET, PP, PA
- Fibre length of 10–40 mm.
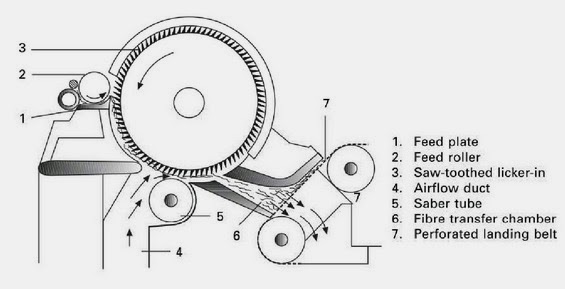
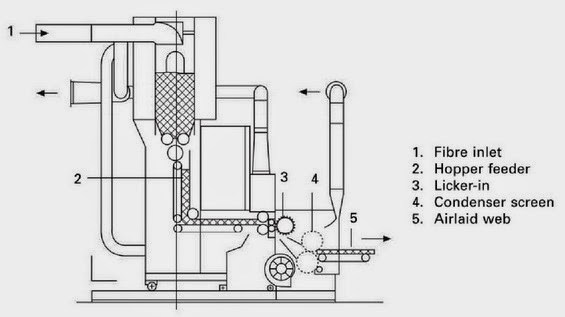
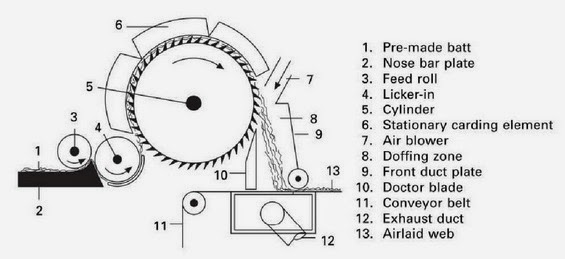
- The turbo-unit TU is either fed by pre-carded webs via a feed plate intake or may be combined with a random card.
- The turbo-roll is equipped with carding segments.
- Aerodynamical web-forming by centrifugal force, doffer fan and suction conveyor
- Lower to medium fibre fineness range
- Staple length: approx. 10 - 80 mm
- Web weight: approx. 25 - 450 g/m 2
- Throughput depending on fibre fineness and fibre type: up to approx. 400 kg/h/m of working width
- Working widths: up to 4.000 mm
- Web speed: approx. 20 - 120 m/min
- Web weight ranges from 300 to 3000 g/m 2
- Production speed of up to 10–15 m/min
- Fibre length should be in the range 20–75 mm
- Cotton, man-made, glass fibres
- Hemp, flax, sisal, coconut
- Bed covers, mats, upholstery and insulation material, carrier material for carpets, industrial and geotextiles as well as furniture textiles
- HIGH ISOTROPICITY
- HIGH LOFT (IF REQUIRED)
- HIGH POROSITY (95–>99%)
- HIGH ABSORBENCY AND WICKING RATE
- SOFT HANDLE
- ADEQUATE TENSILE STRENGTH
- GOOD RESILIENCY (COMPRESSION RECOVERY)
- HIGH THERMAL RESISTANCE.
- Chemical bonding: napkins, table cloths and wipes
- Thermal bonding: nappies (different components, i.e., acquisition layer, distribution layer and absorption core), feminine hygiene/incontinence products and insulation
- Spunlacing: wet and dry wipes for domestic and industrial applications medical textiles (including disposable gowns, curtains, wound-care dressings, bed sheets), filtration media
- Needle punching: interlinings and shoe linings, wadding, medical and hygiene products, geotextiles and roofing felts, insulation felts, automotive components, filters, wipes
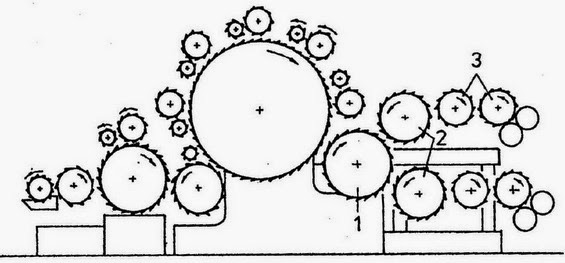
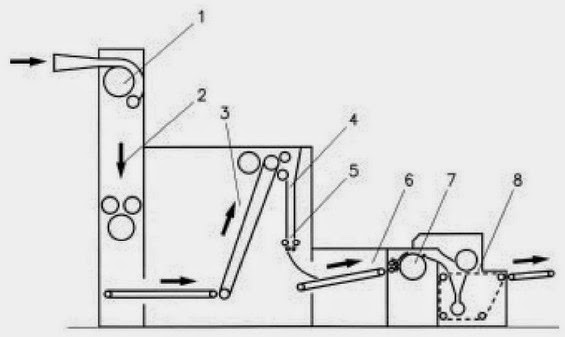
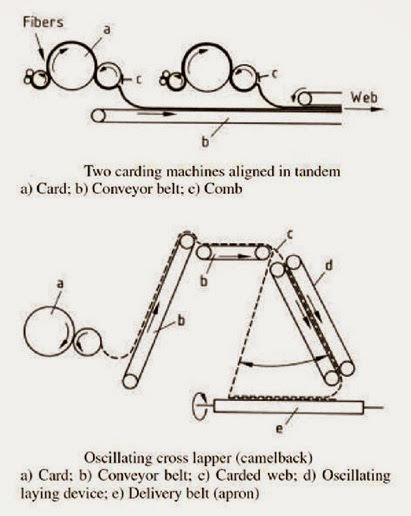
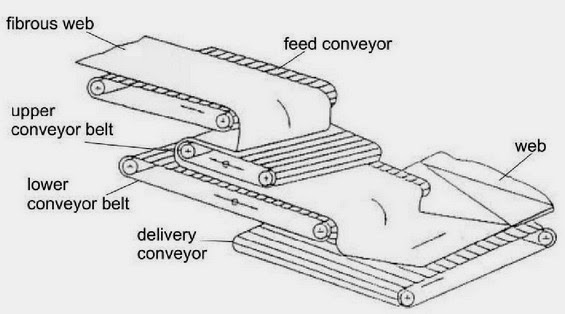
CROSSLAPPER WITH HORIZONTAL LAYING DEVICE Tasks of the web-laying machine
- Increasing the web mass
- Increasing the web width
- Determining the web strength in the length and cross directions
- Improving the end product quality
MERITS AND LIMITATIONS OF CARD – CROSS LAPPING AND AIR LAYING
 |














No Responses to "Airlaid Web Formation Technique"