HIGH PERFORMANCE FIBERS FOR VARIOUS APPLICATIONS
Saddamhusen Jamadar & Santosh Pattekari
D.K.T.E’S TEXTILE & ENGINEERING INSTITUTE,
ICHALKARANJI, INDIA
Email: saddamjamadar75@gmail.com
Saddamhusen Jamadar & Santosh Pattekari
D.K.T.E’S TEXTILE & ENGINEERING INSTITUTE,
ICHALKARANJI, INDIA
Email: saddamjamadar75@gmail.com
INTRODUCTION
The high performance fiber concept came into textile industries during 1950-1970’s. High performance fibers have been developed to offer high strength, high modulus, thermal stability at high temperature, chemical and solvent resistance& number of other properties for their own end use application.
TYPES OF HIGH PERFORMANCE FIBERS
1. CARBON FIBER
- Carbon fiber was first developed in 1963 in the Royal Aircraft establishment.U.K
- Carbon fiber may be defined as a fiber which contains 90% of carbon.
- It is having high flexural rigidity and torsional rigidity.
Manufactured from precursors like PAN, cellulose fiber, pitch fiber & phenolic fiber
It mainly includes 4 stages :
Precursor production
↓
Thermal stabilization between 100-4000C
↓
Carbonization between 700-15000C
↓
Graphitization between 1500-30000C
↓
Thermal stabilization between 100-4000C
↓
Carbonization between 700-15000C
↓
Graphitization between 1500-30000C
TYPES OF CARBON FIBERS
- Ultra high modulus(500GPA)
- High modulus (300-500GPA)
- Intermediate modulus(300GPA)
- Low modulus (
- High tenacity
- DENCITY : 1.8-1.96G/CC
- TENACITY : 22gpd
- ELONGATION: 0.38-1.8%
- MODULUS: 1500-3000gpd
- HIGH FATIGUE RESISTANCE
- GOOD VIBRATION DAMPING
- GOOD ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
- HIGH RESITANCE TO CHEMICAL
- LOI MORE THAN 60%
- HIGH BRITTLE
- LOW IMPACT RESISTANCE
- LOW ABRASION RESISTANCE
- LOOP STRENGTH 0%
- Aerospace
- Road & marine transport
- Automobile hood
- Air craft brakes
- Nuclear field
- Textile machinery
- Medical application
- It is a aromatic nylon Having benzene ring in the molecules
- DuPont has introduced this aramid fiber in order to develop strong high temp resistance fiber
- Nomex first aramid fiber introduced in 1960
DuPont USA
- Nomex® fibre
- Kevlar® fibre
- Technora® fibre
- Teijin conex® fibre
- Twaran® fibre
- It is a synthetic fiber of DuPont corporation that was first created in 1965.
- It contains both aromatic and amide molecular groups.
- Amide groups form a hydrogen bonds between the polymer chains holding them together like a glue.
- Aromatic component have radial orientation , which provides an even higher degree of symmetry and strength to internal structure of fibers
- Spun fibers exhibit a crystalline arrangement with the polymer chains oriented parallel to fiber axis.
- p-phenylene diamine & terephthaloyl chloride are raw materials.
- Undergo low temperature polycondensation reaction.
- The polymer is isolated, neutralized, washed & dried.
- Then subjected to dry jet wet spinning to obtain Kevlar.
- LCP with 90%orientation .
- Tenacity: 23gpd
- Tg : 300 ºC
- Melting point: 540ºC
- Low creep
- Excellent dimentional stability
- High specific strength and modulus
- High kinetic energy
- Good environment stability in sea water, oil, solvent
- Good thermal insulation
- Poor abrasion resistance
- Poor resistance to UV rays
- Armor system
- Rubber reinforcement
- Ropes & cables
- Composites
- Bio-medical & Electronic applications
| TYPE | DENIER | WEAVE | EPI | PPI | GSM | NO.OF PLIES |
| 29 | 1000 | PLAIN | 30 | 30 | 289 | 8 |
| 29 | 1500 | PLAIN | 35 | 34 | 475 | 8 |
| 129 | 840 | PLAIN | 31 | 31 | 231 | 12 |
HIGH PERFORMANCE POLYETHYLENE
DYNEEMA TOYOBO
SPECTRA HONYWELL
STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES:
Light wt body armor for protection from
- It is a thermo plastic fibre .
- It has extremely long chains, with molecular weight numbering in the millions, usually between 3.1 and 5.67 million
 |
| High performance yarn |
- Produced by gel spinning technique
- UHMWPE is synthesized from monomers of ethylene bonded together to form ultra high molecular weight polyethylene.
- UHWMPE molecules tend to have 100,000-250,000 monomers each.
DYNEEMA TOYOBO
SPECTRA HONYWELL
STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES:
- Weak Vander Waals bonds between its molecules .
- Appearance circular and smooth.
- Tensile properties 25-35 gpd 10-15 times more than steel
- Density-0.91g/cc so specific strength is more
- Breaking length is very high(400 km)
- Good Kinetic energy absorption .
Light wt body armor for protection from
- Common handguns 350 m/s
- Heavy terrorist threats 850m/s
- Piercing rifle 900m/s
- Very high fatigue resistance.
- High abrasion resistance
- Biologically inert.
- Good Cut and puncture resistance.
- Resistance to light is poor
- Low LOI
- No moisture absorbency
- Tenacity and modulus decrease drastically at high temperature
APPLICATIONS OF HIGH PERFORMANCE FIBERS :
- Ballistic protection-resistance to impact, high sonic velocity, mechanism of energy absorption
- Gloves, twines, nets-cut resistance, reduced drag resistance
- Heavy duty ropes-reduced backlash on breaking, low elongation
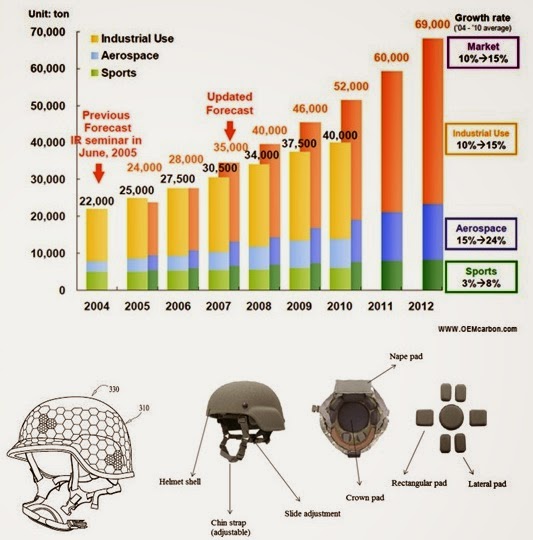 |
CONCLUSION:
When compared with the conventional fibres, most of the high performance fibres are expensive but contribute high added value to the final products. In spite of the high production costs, the high performance fibres are still mainly confined to Europe, America and Japan.
When compared with the conventional fibres, most of the high performance fibres are expensive but contribute high added value to the final products. In spite of the high production costs, the high performance fibres are still mainly confined to Europe, America and Japan.















No Responses to "High Performance Fibers for Various Applications"