Cotton Yarn Manufacturing Process

Ramandeep Singh
B.Tech, Dept. of Textile Engineering
Giani Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus,
Bathinda, Punjab, India
Email: rmnsandhu3335@gmail.com
Spinning:
Spinning is the first steps of textile product processing. The process of making yarns from the textile fiber is called spinning. Spinning is the twisting together of drawn out strands of fibers to form yarn, though it is colloquially used to describe the process of drawing out, inserting the twist, and winding onto bobbins. There are different types of spinning, the most commonly forms of spinning are: Ring, Rotor spinning, Air Jet, Friction etc. Now I will discuss about cotton spinning process.
Flowchart in Blowroom:
 |
 |
| UNIFLOC(A-10) |
- The basic objective of unifloc ix to open the bales into smaller and lighter tuffs or floc.
- To transfer this materials to the various other machine of blowroom line for further processing.
The Unifloc severs the purpose in an unrivalled way the secret lies in the well thought out construction of the take-off unit. The toothed disc of the opening roller are arranged so as to cause a tumbling action therefore by preventing the formation of furrows on the bales..
The setting of unifloc system depend upon two factor:
- Overall production of the unit
- Length of the belt
- Make „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„Trutzschler
- Model „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„Unifloc A10
- Machine weight „„„„„„„„„„„„2700kg
- Max.work of depth „„„„„„„„„1.7m
- Production up to „„„„„„„„„„„,1000kg/h
The uniclean is the efficient cleaning and machine in the first stage after the unifloc . Material coming from unifloc and waste opener is sent to uniclean.
In Uniclean a cylinder equipped with pin which lead the material several times (six times) over a separating surface consisting of triangular grid bar. This process is entirely mechanical.
The cleaning principle separates the tufts exposing dust which is eliminated together with fibers fragment and small trash particles through a special continuous suction system by means of a control panel .The relative waste amount and the cleaning intensity can be entered directly. The cylinder are automatically adjusted according to these values. In combination with the unifloc a separates working point for each assortment can be defined when several types of raw material are being processed.
Technical data:
- Make „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,Reiter
- Model „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„UnicleanB1
- Year „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„ 1992
- M/c weight „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,1220kg
- Waste % „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,1-1.5kg
- Pin roller weight „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,165kg
- Pin roller rotate „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„480-800rpm
- Production up to „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„1000kg
Working Principle:
These work on the principle of passing cotton over different cylinder having relative velocity to each other. cotton is fed in machine through the conveyer belt. Pressure roller provides the limited supply of cotton while the feed roller provides limited as well as proper supply of cotton. In cvt3 are three cylinders first having needle clothing while second and third having metallic clothing. Speed of middle beater is more than first beater while speed of third beater is more than second beater. First beater having needle clothing convert big flocks of cotton in smaller flocks while 2nd and 3rd converts them into individual fibre
Technical data:
- Make „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„Trutzschler
- Model „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,CVT 3
- Year „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„2003
- M/c width „„„„„„„„„„„„„1220mm
- M/c length „„„„„„„„„„„„„2455mm
- 1st beater speed „„„„„„„„,960-1760rpm
- 2nd beater speed „„„„„„„„1840-2804rpm
- 3rd beater speed „„„„„„„„,1790-3570rpm
- Beater dia „„„„„„„„„„„„„,250mm
- Air intake rate „„„„„„„„„„,3000+10%m3/h
Working Principle:
Fast moving Cotton having dust particles is allowed to hit the perforated wall where cotton being bigger in size is stopped there while small dust particles because of inertia travel by the small holes of the perforated wall. So dust gets separated from the cotton.
Technical data:
- Make „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,Trutzschler
- Model „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„Dustex 38
- M/c width „„„„„„„„„„„„1864mm
- Total length „„„„„„„„„„„2150mm
- Total height „„„„„„„„„„„2650mm
- Material suction „„„„„„„„200-250pa
- Dust extraction „„„„„„„„,300-400pa
- Material feed „„„„„„„„„„150-200pa
Carding is the heart of the spinning industry. Carding is carried out by passing entangled fibres between closely spaced surfaces of cylinder and flats covered with sharp metal teeth .The surfaces are moved relative to each other and so the fibres are disentangled .
OBJECTIVES OF CARDING:
- The carding machine opens the folks of fibres to individual fibre stage.
- Removal of impurities.
- To remove the neps and short fibres from cotton.
Material flow:Setting of card
| Sr.no. | Set point | Gauge(thou) |
| 1. | Feed plate to1st l-in | 30 |
| 2. | Mote knife to l-in | 40 |
| 3. | Combing segment to 1st l-in | 30 |
| 4. | Mote knife to 3rd l- in | 60 |
| 5. | 3rd l-in to cylinder | 7 |
| 6. | Back bottom plate | 34 |
| 7. | Back sweb clearer | 16/14 |
| 8. | Back mote knife | 20 |
| 9. | Cylin-to flat guage | 8,8,7,7, |
| 10. | Front top plate | 3/6 |
| 11. | Front top sution hood | 13 |
| 12. | Cylinder to doffer | 4/5 |
Paramiters
Although the fibres are separated up to individual state but they are in random disorganized manner in the card sliver. Draw frame straightens and align the fibre along the axis of the sliver in order to have strong and even spinningTechnical data:
Objective of lap preparation:
TASK OF THE COMBER:
Production of the comber is dependent upon the following:
Objectives:
- Feed roll dia 100mm
- 1st l-in dia 172.5mm
- 2nd l-in dia 172.5 mm
- 3rd l-in dia 172.5mm
- Cylinder dia 1287mm
- Doffer dia 700mm
- CYLINDER SPEED=(494-604)rpm
- LICKER-IN SPEED:
- 1ST=945-1230
- 2ND=1467-1909
- 3RD=1922-2502
- Doffer speed (120-180)rpm
- DRAFT=60-250fold (120fold)
- FLAT SPEED=320mm/min
- Dfk pressure 0-999pa (300pa)
- Fineness .066-.197Ne (.135Ne)
- Ppsi cylinder rolls 860
- Ppsi doffer 360
- PRODUCTION = 41-52.5kg/h
- Motor pulley
- Cylinder pulley
- Licker-in pulley
- Change wheel for draft between doffer and stripping roll
- Change wheel for draft between stripping roller and squeezing roller
- Change wheel for draft between calendar roller and coiler roller
- Flat speed change gear
- Can diameter - 24 inch
- Height (from ground) - 48 inch
- Check for flat loading
- Abnormal sound in m/c
- Machine heating up
- Smooth web material
- Chute filling
- Waste suction
- Safety doors and covers
- No air leakages
- centrally chute feed system for entire card
- automatic can changer
- total coverd body
- Genral cleaning 3days
- Full cleaning 1month
- Oprater 1
- Reliver 1
- Floor cleaner 1
Although the fibres are separated up to individual state but they are in random disorganized manner in the card sliver. Draw frame straightens and align the fibre along the axis of the sliver in order to have strong and even spinningTechnical data:
- Manufacturer: Rieter.
- Model: SB2
- Year: 1994
- No. of machines: 2
- Input material: card sliver
- Total no of cans: 6x2=12
- No. of doublings: 6
- No of coiling head: 2
- Output: sliver
- Drafting system 3/3
- Total draft range 4.24-12.15
- Delivery speed 650- 800m/min
- Length of delivery 10750m/min
Objective of lap preparation:
- To make even feed for comber
- To present sliver hooks as leading hooks to the comber
- To make the fibre more parallel
- Manufacturer: Rieter
- Model: E32
- No of machines: 2
- No of doubling 26
- No of delivery 1
- Drafting system 3/3
- Draft: 1.36-2.2
- Drafting system: 2 zone drafting system
- Delivery speed 124m/min
- Sliver count range: 3.3-6kTex
- Doubling: up to 28 folds
- Length of delivery 240m
- yarn evenness
- strength
- cleanness
- smoothness
- visual appearance
TASK OF THE COMBER:
- To produce an improvement in yarn quality, the comber must perform the following operation.
- elimination of short fibres as noil
- elimination of remaining impurities
- elimination of neps
- The basic operation of the comber is to improve the mean length or staple length by removing the short fibres.
- Trailing hooks from carding should be fed as leading hooks to reduce long fibre loss in the noil
- Feeding, lap is fed by feed roller
- fed lap gripped by the nipper
- gripped lap is combed by circular comb
- detaching roller grips the combed lap and moves forward
- while the detaching roller delivers the material, top comb comes into action to further clean the lap
- While going back, nipper opens and receives a new bit of lap.
- Forward feed (concurrent feed):Feed of the sheet into the nippers occurs while the nippers move towards the detaching roller
- Backward feed (counter-feed): Feed of the sheet occurs during return of the nippers.
Production of the comber is dependent upon the following:
- N- Nips per min
- S- feed in mm/nip
- G- lap weight in g/m
- K- Noil percentage
- A- tension draft between lap and feed roller(from 1.05 to 1.1)
- E- efficiency
- No of heads=8
- Noil %=16.5%
- Nips/min=450-458
- Feed/nip=4.7-5.2mm
- Length of delivery=6290
- Delivery rate=215m/min
- Drafting system=3/3
- Noil suction pressure=12-15mm of water column
- Time taken to fill up a can=29min
- Sliver weight=4.720ktex
- Manufacturer: Rieter
- Model: E65
- Year: 2006
- Nos. 8
- Lap width: 270-300mm
- No. of lap per machine: 8
- Batt weight per meter: 60-80 gm/mt
- Lap diameter: up to 650mm
- Feed per nip: 4.3/4.7/5.2/5.9mm
- Noil: 8-25 %
- Drafting system: 3/5
- Doubling: 8 fold
- Sliver weight: 3-6 kTex
- Break draft: 1.14-1.5
- Total draft: 9.0-23.1
- Loading: pneumatic
- Top detaching roller: 3-4bar
- Drafting system front roll: 2.5-3bar
- Drafting system 2nd and 3rd rolls: 3.5-4.5bar
Objectives:
- To make sliver with maximum possible evenness.
- To make required hank for input in speed frame.
Material flow on the Drawframe is given by following flowchart
Autolevelling: When sliver is passed through the scanning rollers then it measures the thickness of material. Scanning rollers are connected to the signal generator which converts thickness variation in the electronic signals. These signals are compared by standard value by the electronic memory and then it gives the signal to the servo drive to maintain the proper draft with particular thickness.
Technical data:
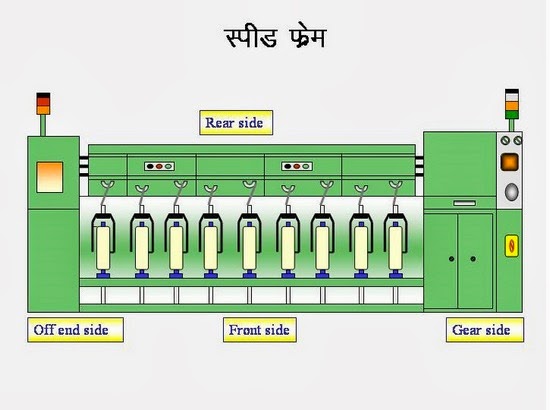
Simplex is the intermediate machine between draw frame and the ring frame. The purpose of the roving frame is to produce out of the draw frame sliver a well prepared roving of required as well as the prepare bobbin for the ring frame .
OBJECTIVES OF ROVING FRAME
Technical Data:
OBJECTIVES OF RING FRAME
It performs mainly two operations:
Technical data:
- Manufacturer: Rieter.
- Model: LRSB851&RSB 851
- Drafting arrangement: „„„„„„„,3/3 3/3 Draft range: 5.5-11.5 5.5-11.5
- Sliver hank delivered: „„„„„„„,0.12-0.19
- Top rolls(mm): „„„„„„„,26x38x160
- Dia of bottom rollers: „„ 40,30,30
- Break draft „„„„„„„„„,0.99-1.03
- No of machines „„„„„„, 7
- Sliver Break stop motion,
- Sliver lapping stop motion,
- Can exhaust stop motion,
- Safety door stop motion.
Simplex is the intermediate machine between draw frame and the ring frame. The purpose of the roving frame is to produce out of the draw frame sliver a well prepared roving of required as well as the prepare bobbin for the ring frame .
OBJECTIVES OF ROVING FRAME
- To draft the material to the required linear density.
- To insert minimum required level of twist.
- To produce a suitable package for the next process.
- To reduce the thickness of the sliver.
 |
- Model: „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,LF1400 &LF1400A
- Manufacturer:„„„„„„„„„„„„„ LMW
- Year: „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,1994
- Total no of spindles „„„„„„„„„120
- Drafting system „„„„„„„„„„„„3/3&4/4 drafting system
- Spacer size „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„3.5to11mm
- Bottom apron size „„„„„„„„„„76*40*1.0mm
- Bottom roll dia „„„„„„„„„„„„,27-30mm
- Top apron size „„„„„„„„„„„„,38.5*41.5*1.0mm
- Cradle „„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„„,31mm
- Rubber cots „„„„„„„„„„„„„„29mm
- Roller gauge „„„„„„„„„„„„„„45/58-45/68
- Saddle gauge „„„„„„„„„„„„„,51/56-51/66
OBJECTIVES OF RING FRAME
It performs mainly two operations:
- To convert roving into yarn of required count.
- To wind yarn on the cop.
- Manufacturer: KTTM
- Model: RXI-240
- Year: 1994
- Total no. of machines: 23
- No of spindles per machine: 864
- Spindle speed: 20000 rpm (max)
- Manufacturer: LAKSHMI-RIETER Model: G 5/1
- Year: 1994
- Total no. of machines: 25
- No of spindles per machine: 864
| COUNT | BLEND | ROVING HANK | D.C. | B.DR | TC | TPI | T.M. | SPACER |
| 2/40sPCCW | 65/35 | 1.05 | 45 | 1.25 | 39 | 23.4 | 3.7 | 2.8mm |
| 40sPCCH | 52/48 | 1.05 | 46 | 1.25 | 51 | 21.9 | 3.46 | 2.8mm |
| 40sPCCW | 35/65 | 1.2 | 51 | 1.25 | 43 | 25.95 | 4.1 | 2.5mm |
| 18sVISCOSE | | 1.7 | 57 | 1.25 | 44 | 14.05 | 3.31 | 3.5mm |
| 40sPCCH | 40/60 | 1.05 | 45 | 1.25 | 49 | 22.76 | 3.6 | 2.8mm |



























No Responses to "Cotton Yarn Spinning Process"